WUNRN
Gender Impacts of the EU Employment Crisis - Youth/Young Women
Issues +
________________________________________________________
THE PRICE OF AUSTERITY - THE IMPACT
ON WOMEN'S RIGHTS & GENDER EQUALITY IN EUROPE
Direct Link to Full 20-Page 2012
Presentation:
___________________________________________________________
European Commission - Eurostat
EUROPE UNEMPLOYMENT STATISTICS
Data up to November 2013. Most recent data: Further Eurostat information, Main tables and Database.
Unemployment levels and rates move in a
cyclical way, largely related to the general business cycle. However, other factors such
as labour market policies and demographic developments
may influence the short and long-term evolution as well. This
article gives an overview of statistical information for unemployment in the European Union (EU) since the year
2000, starting with the most recent developments.
http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/statistics_explained/index.php/Glossary:Labour_force_survey_(LFS)
Monthly unemployment
and employment series are calculated first at the level of four categories for
each Member State (males and females 15-24 years, males and females 25-74
years). These series are then seasonally adjusted and all the national and
European aggregates are calculated. Monthly unemployment figures are published
by Eurostat as rates (as a percentage of the labour force) or levels (in
thousands), by gender and for two age groups (persons aged 15-24, and those
aged 25-74). The figures are available as unadjusted, seasonally adjusted and trend series. There are monthly estimates for all
EU-28 Member States except for Latvia. Data for the EU-28 aggregate start in
2000 and for the euro area (EA-17) in 1995; the starting point for individual
Member States varies.
___________________________________________________
YOUNG WOMEN & EMPLOYMENT
Gender Disaggregation of Data?
Gender Lens for Suggested Solutions?
Policies & Programs for Many
Young Women Who
Must Balance Family
& Work Responsibilities?
___________________________________________________________
EDUCATION TO EMPLOYMENT: GETTING
EUROPE'S YOUTH INTO WORK -
Youth
Unemployment aross the European Union Remains Unacceptably High, to the
Detriment of Current& Future Generations.
Addressing
It Requires Understanding Causes& Relentlessly Pursuing Solutions
January 2014 - The problem of youth
unemployment in the European Union is not new. Youth unemployment has been
double or even triple the rate of general unemployment in
To understand this disconnect and what can be done about it,
McKinsey built on the methodology used in our 2012 publication, Education to Employment: Designing a System that Works.1 We concentrated on four
broad questions:
- Is the scale of the
youth-unemployment problem in Europe a result of lack of jobs, lack of
skills, or lack of coordination?
- What are the obstacles
that youth face on their journey from education to employment?
- Which groups of youth
and employers in Europe are struggling the most?
- What can be done to
address the problem?
To answer these questions, we surveyed 5,300 youth, 2,600
employers, and 700 postsecondary-education providers across 8 countries that
together are home to almost 73 percent of Europe’s 5.6 million jobless youth:
Our research led us to the following answers:
1. While there are more people looking for work,
employers in Europe
cannot find the skills they need.
Clearly, the lack of availability of jobs in
Yet despite this availability of labor, employers are
dissatisfied with applicants’ skills: 27 percent reported that they have left a
vacancy open in the past year because they could not find anyone with the right
skills. One-third said the lack of skills is causing major business problems,
in the form of cost, quality, or time. Counterintuitively, employers from
countries where youth unemployment is highest reported the greatest problems.
So why is it that young people are not getting the skills that employers need?
One reason is the failure of employers, education providers, and young people
to understand one another. To cite our 2012 report, they operate in “parallel
universes.”
In
2. Youth face three significant hurdles.
The education-to-employment (E2E) path can be described
as a road with three intersections: enrolling in postsecondary education,
building the right skills, and finding a suitable job. The problem is that in
When it comes to enrolling in further education, the most
significant barrier in
At the second intersection, young people are often not
learning a sufficient portfolio of general skills while they study, with
employers reporting a particular shortage of soft skills such as spoken
communication and work ethic. Employers and providers are not working together
closely to address this.
At the final intersection, young people find the
transition to work difficult. One-third fall into interim jobs after
graduating, and many more struggle to find a job at all. Many lack access to
career-support services at their postsecondary institution. Many more do not
pursue a work placement, in spite of this being a good predictor of how quickly
a young person will find a job after his or her studies are completed.
3. The E2E structure is failing for young people and for
small businesses.
To refine our understanding of the issue, we divided
young people and employers into segments to examine different interventions to
achieve better education-to-employment outcomes Specifically, we looked at how
much support young people received on their path from education to employment,
and the extent of their desire to develop skills that would make them more
employable (Exhibit 1).
Exhibit 1
Few young people have a
successful journey to employment.
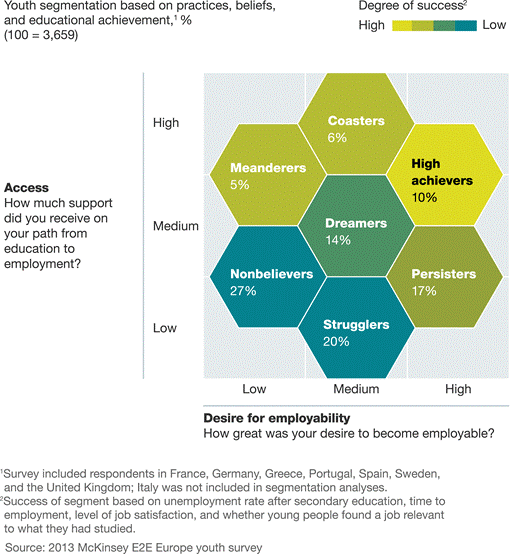
Only one of our segments, the so-called high achievers,
which represent 10 percent of the youth surveyed, achieves a good employment
outcome. This group succeeded because the young people in it receive a strong
education and good information; they also focus on finding opportunities to
build job skills. Another two segments, representing 11 percent of youths
surveyed—what we call “coasters” and “meanderers”—receive strong support but
are less motivated and end up only moderately satisfied with their job
outcomes. The remaining four segments (79 percent) are frustrated by a lack of
support and unhappy at their prospects. They exhibit different responses to
these circumstances, from fighting for every opportunity they can get (but
rarely succeeding) to losing heart and leaving education at the first
opportunity.
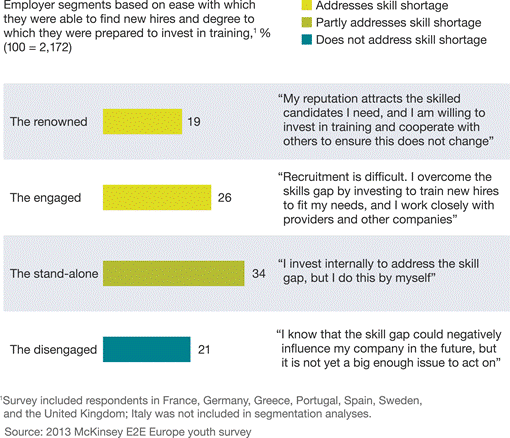
We based our employer segmentation on the ease with which
employers could find new hires and the degree to which they were prepared to
invest in training (Exhibit 2). While two of the four segments are basically
satisfied with their workforce, they start from very different places. One
segment, representing 19 percent of employers, is able to attract strong
candidates and invests substantially in training new hires. A high proportion
of the companies in this group are large companies with an established market
position. The other satisfied segment, representing 26 percent, finds it
difficult to attract strong candidates but develops a strong workforce through
training and partnerships. Of the two less satisfied segments, one (34 percent)
reports moderate satisfaction but tackles the skills problem alone. The other
(21 percent) is disproportionately made up of small businesses and is the least
satisfied. This group struggles to find people with the right skills yet either
does not, or cannot, invest in training.
Exhibit 2
Less than half of
employers are satisfied by their workforce’s skill levels.
In contrast to the findings of our global survey, in
4. There are proven ways to improve the E2E journey.
Innovate with design, course delivery, and financing to make education more
affordable and accessible
To reduce the cost of courses, one solution is to break
up degree or vocational programs into individual modules that focus on building
a particular set of skills while still counting toward a degree or formal
qualification. Each of these modules would be short (weeks or months) and
self-contained, enabling young people to combine and sequence them in the order
that makes most sense for their career aspirations. This model also enables young
people to take a break in their studies to work for a period, and then return
and pick up where they left off.
To improve financing, governments and private financial
institutions can offer low-interest loans to students pursuing courses that
have a strong employment record; they can also explore initiatives that allow
young people to repay loans in the form of services, such as tutoring younger
students. Employers can play a role by promising jobs to young people
(following a rigorous recruitment process) and then assuming responsibility for
part or all of the costs of education in return for the opportunity to select
the most successful graduates, trained with the most relevant skills they need.
This latter option is only likely to be successful, however, for employers in
sectors that face either a skills scarcity or high employee churn.
Focus young people, employers, and education providers on improving
employment readiness
Young people, employers, and providers must change how
they think about the E2E process. To make rational decisions, young people need
to think more strategically about their futures. This is particularly important
in
Education providers should focus more on what happens to
students after they leave school. Specifically, they should track graduates’
employment and their job satisfaction. To improve student prospects, education
providers could work more closely with employers to make sure they are offering
courses that really help young people prepare for the workplace.
Employers cannot wait for the right applicants to show up
at their doorsteps. In the most effective interventions, employers and
education providers work closely to design curricula that fit business needs;
employers may even participate in teaching, by providing instructors. They
might also consider increasing the availability of work placements and
opportunities for practical learning. Larger enterprises may be able to go
further, by setting up training academies to improve required skills for both
themselves and their suppliers.
Build the supporting structures that allow the best interventions to scale
up
At a national level in
Involve the European Union
To help the most successful interventions reach the
greatest number of young people, the European Union has a critical role to play
in three areas:
- Information.
The European Union could develop and share a more comprehensive
labor-market platform incorporating the most relevant data to capture
employment trends in each sector and region. This would help institutional
decision makers, employers, and job seekers make better decisions, for
instance, by helping users understand the implications of the data—whether
on the courses they should offer as an education provider or the skills
gaps they should try to fill as a group of employers within an industry.
- Mobility. The European Union can improve
educational and labor mobility by working to make vocational
qualifications transferable across borders, as has already largely been
achieved in the university-education process in Bologna.
- Sharing relevant practices on matching labor-market
demand and supply. The European Union is in the best
position to take the lead on helping national public-employment services
compare their successful interventions, and then disseminate and promote
those that are relevant to similar-context countries.
Youth unemployment is a profound challenge to the future of
For more
on this research, download the full report, Education to Employment:
Getting Europe’s Youth into Work (PDF–7,235KB).